| Home |
| Governmental Income |
| Income |
| Poverty |
| Race |
| Crime |
| Male Partners |
| Maps |
| Graphs |
| Data Tables |
| Works Cited |
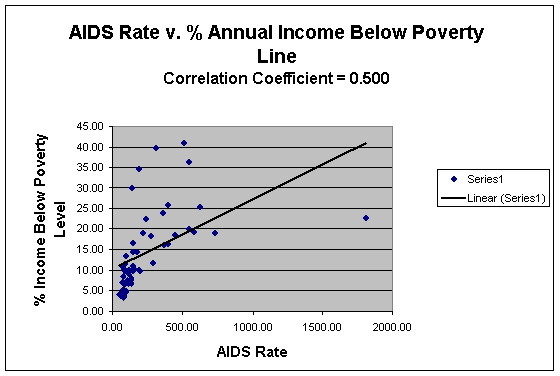
Poverty has a clear and strong relationship with cumulative AIDS rates. The percent of community members in each zip code with income under the poverty line and cumulative AIDS rates constructs a correlation coefficient of 0.50, marking an obvious link between AIDS and poverty within the Pittsburgh region as it hits both the 95% and 99% intervals (Tables 1.1, 1.7; Graph 1.6; Maps 1.1, 1.3). The poverty line is determined by the census bureau through using "a set of money income thresholds that vary by family size and composition to detect who is poor" (United States Census Bureau). In addition, “if the total income for a family or unrelated individual falls below the relevant poverty threshold, then the family or unrelated individual is classified as being "below the poverty level"( United States Census Bureau). The thresholds for poverty change every 10 years along with the census. In 2000, the poverty threshold for a five person family with three children was set at 21,065 (U.S. Census Bureau, Housing and Household Economic Statistics Division).

Households in East Liberty

East Liberty
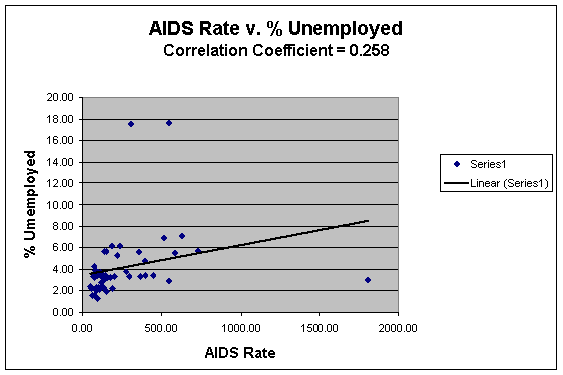
While poverty provided a significant correlation, unemployment did not. At a coefficient of 0.26 the percent unemployed in Allegheny County does not correlate significantly with cumulative AIDS rates (Tables 1.1, 1.8; Graph 1.7). This in essence, reveals that unemployment is not the primary issue with poverty and cumulative AIDS cases in the Pittsburgh region. Instead, it implies that there is some other underlying factor contributing to the poverty and AIDS rates in the Allegheny community.
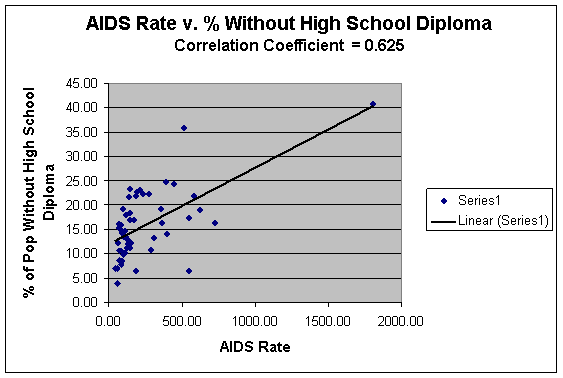
This concealed contributing factor could be presented in the percent of the population with less than a high school diploma. When this educational aspect is correlated with the cumulative AIDS rates in Allegheny County, the coefficient presented lies at 0.625 (Tables 1.1, 1.11; Graph 1.11; Maps 1.1, 1.6). This coefficient proves to be much higher than the significance level of 0.451 - by 0.174 - and leads one to believe that perhaps the lack of education, which correlates with AIDS rates as well, could possibly be the reasons for this significant link with poverty and cumulative AIDS rates. Seeing as both these social issues correlate with cumulative AIDS rates, it could be inferred that they have direct links with one another as well. Therefore, lack of education could be influencing poverty within these targeted communities with high AIDS rates.