 Silicates
Silicates
- Si-tetrahedra: 50/50 mix ionic and covalent bonds
- tetrahedra are never links to one another by more than one oxygen
-if more than one O-edge sharing - Si ions would be too close together=unstable
Nesosilicates: island silicates - SiO4
ex: olivine
- very resistant to weathering
-Aluminum silicates: 3 polymorphs - under different temp. and press. conditions, thus
good indicators of formation environment
Al2O.SiO4
|
kyanite
|
andalusite
|
sillimanite
|
high press
|
low temp
|
high temp
|
-olivine: cleavage is irregular - no preferred plane of weakness
*alters to serpentine (a phyllosilicate)
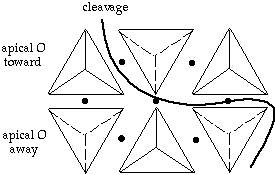
Sorosilicates: double tetrahedra linked by common O - Si2O7
ex: epidote -actually mix of isolated tetrahedra and "soro-linked" tetrahedra
Cyclosilicates: 3, 4, 6, or 12 tetrahedra linked - Si6O18
ex: tourmaline, beryl
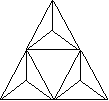 tourmaline - trigonal/rhombohedral
tourmaline - trigonal/rhombohedral
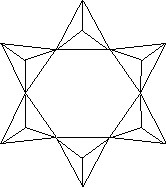 beryl - hexagonal
beryl - hexagonal
Inosilicates:
- "thread" - single chain - linked by 2 O's of base - higher temp.
- double chain - two linked chains with a large hole between them
-filled by large anions: OH-, Cl-, F-
-amphiboles contain water (OH-) in holes - found at lower temps
-can drive water out of structure of amphiboles with heating - form
pyroxenes
Phyllosilicates: "flaky"
-2 components: tetrahedral sheet & octahedral sheet
-Clay minerals: derived as weathering products
kaolinite, illite, vermiculite, smectite
Tectosilicates: framework - tetrahedra linked by every one of 4 oxygens
ex: SiO2
-low quartz - trigonal or rhombohedral
-high quartz - hexagonal
Varieties:
- cryptocrystalline: flint, chert, agate, jasper, chalcedony, onyx
-very low temp environments - even sedimentary
- crystalline: (macrocrystalline): quartz, tridymite, coesite, cristobalite,
stishovite
-occurrence depends on temp and press conditions
-displacive transformation: *573oC - cooling through this temp
(high to low), get rapid and reversible transformation which involves a warping
or twisting of bonds rather than breaking of bonds
-reconstructive transformation: slow & irreversible - bonds broken and
reformed
Stability Field Diagram:
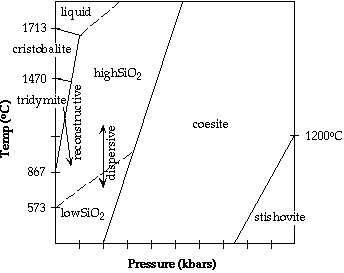
|
http://classes.colgate.edu/rapril/geol201/
Questions to:
rapril@mail.colgate.edu
Copyright 1997 © Colgate University.
|
|



 tourmaline - trigonal/rhombohedral
tourmaline - trigonal/rhombohedral beryl - hexagonal
beryl - hexagonal