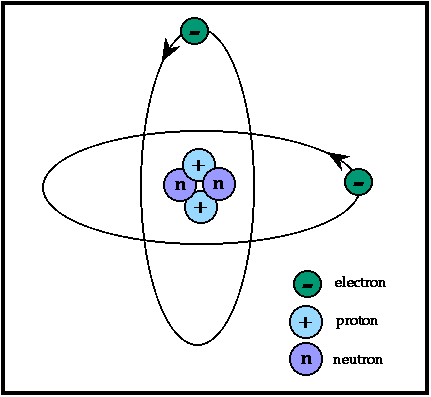
The Effective Radius of an atom or ion
is determined by the distance between the centers of adjacent atoms or ions
in a crystal structure.
This distance is not fixed because electron positions are not fixed and therefore,
the radii really represent the area around the nucleus where
there is a good probability of finding orbiting electrons.
|
Interionic Radii or "Bond Length" is calculated using
Coulomb's Law:
where: F = atrractive force
k = constant
q = charge on ion
r = interionic radius
|
|
Click Here for a
Periodic Table of the Elements
with Atomic and Ionic Radii
|
|

